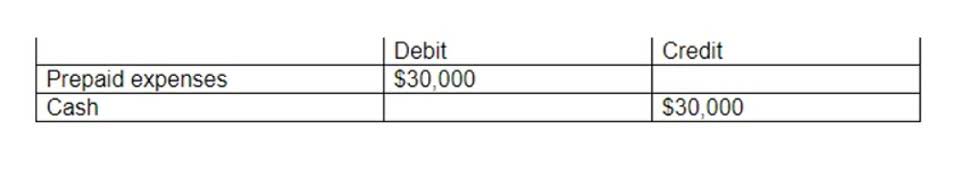
Unrestricted net assets are assets contributed by donors to a nonprofit entity that have no restrictions placed on their use. This is the most sought-after type of asset, since it can be used for administrative and fundraising activities. The typical nonprofit entity structures its fund raising activities to encourage donors to make unrestricted asset donations. However, it doesn’t really matter where the revenue is coming from, as long as the unrestricted net assets amount is positive and it positively contributes to the overall financial health of the non-profit organization.
- In for-profit entities, equity represents the owners’ residual interest in the company after liabilities are deducted from assets.
- Most of the organizations receive unrestricted revenues through donations, fees for services, investment income, ticket sales, or membership income.
- This statement is essential for assessing the nonprofit’s ability to generate cash to meet its obligations and sustain its operations.
- By accurately recording the release of net assets, nonprofits can provide a clear picture of their financial health and resource allocation.
- They serve as a reserve that can be utilized to cover operational costs, invest in growth opportunities, or weather unforeseen challenges.
- In the realm of financial management, organizations often strive to enhance their unrestricted net assets while ensuring long-term fiscal sustainability.
Managing and Reporting Unrestricted Net Assets in Nonprofits
This type of release is particularly beneficial for long-term planning, as it provides a predictable timeline for when additional resources will become available. It also allows nonprofits to align their financial strategies with donor expectations, ensuring that funds are utilized in a timely and effective manner. From a financial perspective, unrestricted net assets provide a cushion against unexpected expenses or economic downturns. They serve as a reserve that can be utilized to cover operational costs, invest in growth opportunities, or weather unforeseen challenges.
- These assets can play a significant role in determining the financial health and long-term stability of an entity.
- This statement must also segregate activities based on the presence or absence of donor restrictions, offering a detailed view of how funds are generated and expended.
- For donors, the transparent handling of these funds can build trust and encourage continued or increased contributions.
- Regardless of the action that gives rise to a classification of assigned fund balance, formal action is not required to reverse that classification.
- This strategic planning ensures that the organization can demonstrate effective use of funds while maintaining a stable financial outlook.
Implications for Stakeholders
Because of the current financial resources measurement focus of governmental funds, fund balance has historically been considered a measure of available what are unrestricted net assets expendable financial resources. This is a particularly important measure in the general fund because it reflects the primary functions of the government and includes both state aid and local tax revenues. This is a significant departure from the decades-long approach of classifying fund balance more from an “available for appropriation” perspective.

Accounting Standards for Restricted Net Assets

The statement of activities, which details the nonprofit’s revenues and expenses, also reflects the impact of released net assets. When funds are reclassified, they are typically reported as revenue in the unrestricted net assets section. This can lead to a noticeable increase in total revenues, providing a more comprehensive view of the organization’s financial performance. By accurately reporting these changes, nonprofits can offer a transparent account of how donor contributions are being utilized, thereby reinforcing donor confidence and fostering long-term support. Temporarily restricted net assets are funds that donors have earmarked for specific purposes Accounting For Architects or projects, but only for a limited period. For example, a donor might specify that their contribution be used for a particular program within the next fiscal year or for a capital project that will be completed over several years.

Temporarily Restricted Net Assets
Nonprofits often use specialized accounting software, such as QuickBooks Nonprofit or Blackbaud Financial Edge, to streamline this process. These tools offer features tailored to the unique needs of nonprofit accounting, including automated journal entries and real-time financial reporting. By leveraging such software, organizations can ensure that their financial records are both accurate and up-to-date, facilitating better decision-making and compliance with accounting standards. In contrast, net assets in nonprofit organizations represent the residual interest of the entity itself, as there are no shareholders. Instead, net assets indicate the organization’s capacity to carry out its mission and sustain its operations. For example, while a for-profit company might reinvest equity to expand its market share, a nonprofit would use its net assets to enhance program delivery, support community initiatives, or invest in long-term sustainability projects.

Effective management of unrestricted net assets is crucial for covering operational costs, such as salaries, utilities, and administrative expenses, ensuring the organization can function smoothly and respond to unforeseen challenges. On the balance sheet, the shift from restricted to unrestricted net assets can enhance the organization’s liquidity and financial flexibility. Unrestricted QuickBooks net assets are often viewed as a measure of financial health, as they represent funds that can be used at the nonprofit’s discretion. An increase in unrestricted net assets can signal to stakeholders that the organization is in a strong financial position, capable of responding to immediate needs and opportunities.